Kepler-36 Atmospheric Escape
Overview
Loss of a hydrogen envelope due to stellar XUV stripping.
Date |
06/28/18 |
Author |
Rodrigo Luger |
Modules |
AtmEsc STELLAR |
Approx. runtime |
31 seconds |
Hydrogen-rich planets that are close to their host star can lose significant mass as the XUV radiation from the host star imparts enough energy for individual atoms to acheive escape velocity. In this example, VPLanet simulates atmmospheric loss for the case of Kepler-36 b, which is considerably smaller in radius than its very nearby companion, Kepler-36 c. Lopez & Fortney (2013) argue that this radius dichotomy can be explained by XUV winds, and VPLanet reproduces that result, see Figure 3 in Lopez & Fortney (2013) .
To run this example
Note
You might need to install tqdm:
pip install tqdm
python makeplot.py <pdf | png>
Expected output
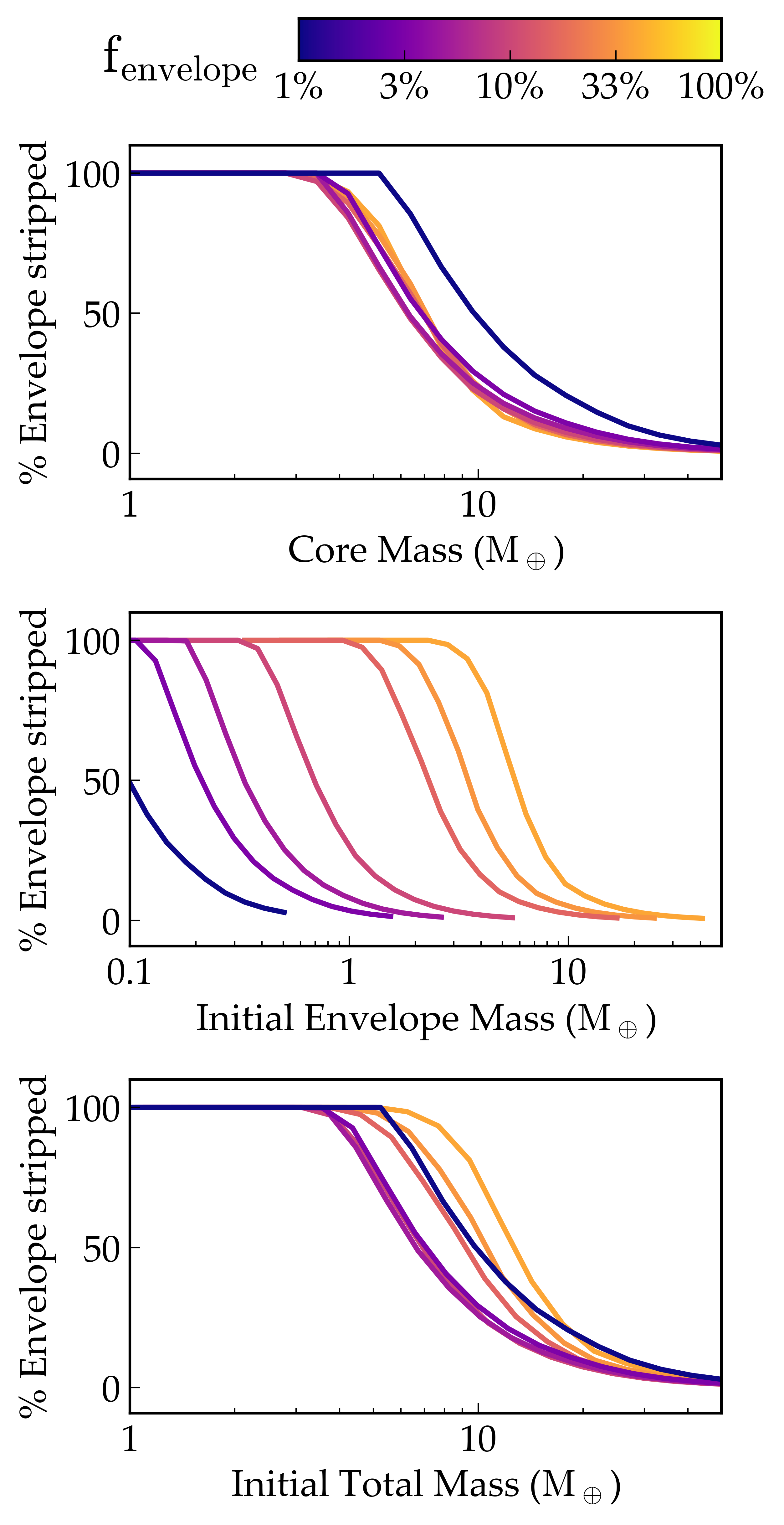
Percentage of the planet’s gaseous enveloped stripped via hydrodynamic escape as a function of core mass (top), initial envelope mass (center), and initial total mass (bottom), for different initial envelope mass fractions (colors). The core mass is the best predictor of the amount of gas that is stripped by hydrodynamic escape.