Water Loss on Venus
Overview
Water loss on Venus from thermal escape processes.
Date |
07/25/18 |
Author |
Rodrigo Luger, Rudy Garcia |
Modules |
AtmEsc STELLAR |
Approx. runtime |
49 seconds |
The Sun’s XUV radiation likely removed water from Venus early in the history of the Solar System. If Venus was in a runaway greenhouse, then water would be in the stratosphere where it can be photolyzed and the hydrogen can escape. Watson et al. (1981) estimated 280 Myr, but did not account for early activity. Including that effect, VPLanet predicts a desiccation timescale of about 100 Myr.
To run this example
python makeplot.py <pdf | png>
Expected output
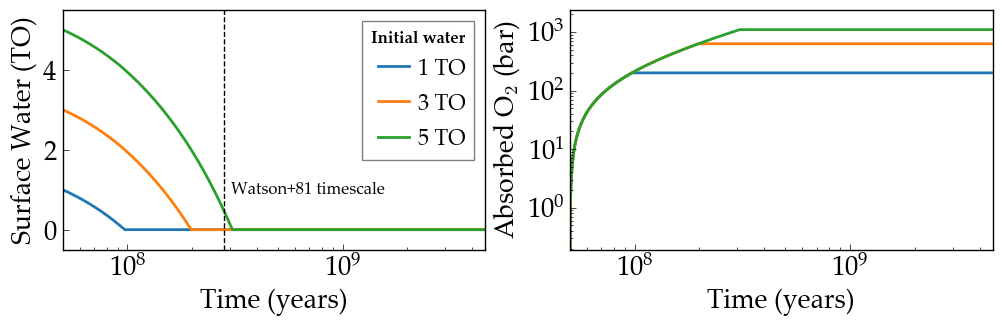
Evolution of the surface water content (left) and amount of oxygen absorbed by the surface (right) as a function of time for three different initial surface water inventories. The vertical dashed line is the Watson et al. (1981) timescale for the desiccation of Venus.
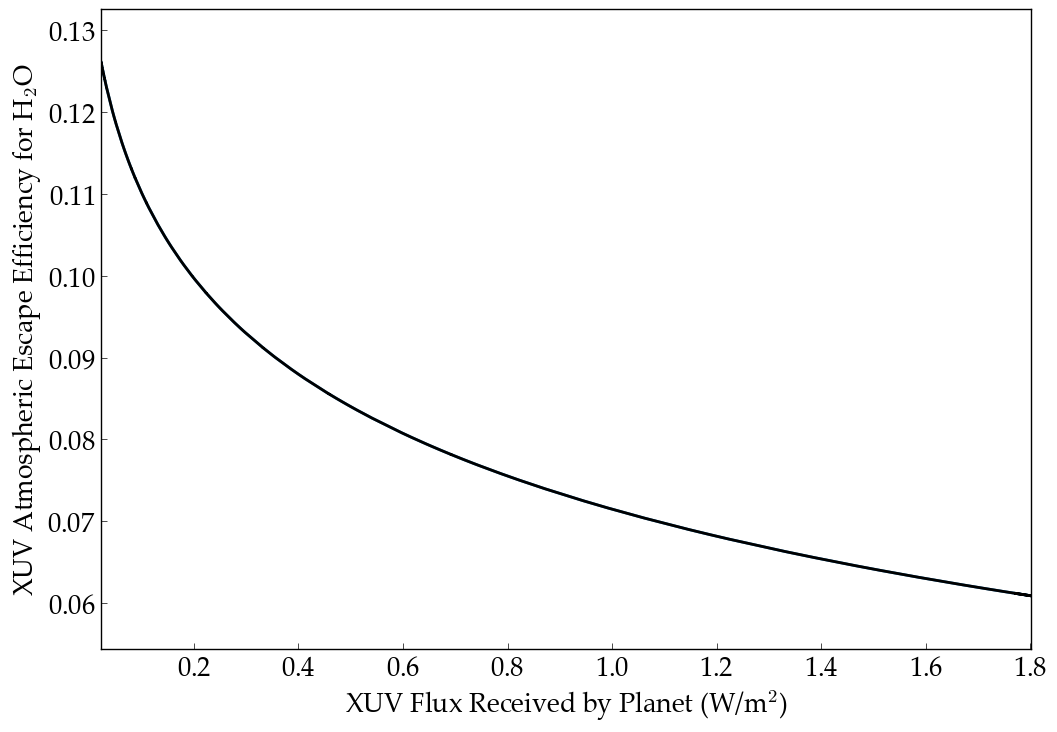
The scaling of the atmospheric escape efficiency for H2O as a function of the XUV flux received by the planet as reported by Bolmont et al. (2017).